PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI

Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Yeungnam Med Sci > Volume 40(1); 2023 > Article
-
Original article
Auricular acupuncture for sleep quality in participants with mental and behavioral disorders due to prior multiple drug use: a retrospective consecutive case series -
Yuri Gimelfarb
 , Eran Goldstien
, Eran Goldstien
-
Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science 2023;40(1):78-85.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00542
Published online: November 28, 2022
Hospital Administration, AMHC, affiliated with Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Bat Yam, Israel
- Corresponding author: Yuri Gimelfarb, MPH AMHC administration, affiliated with the Sackler Faculty of Medicine of Tel Aviv University, 15 KK"L Street, Bat Yam 5943602, Israel Tel: +972-3-555-2749 • Fax: +972-3-555-2787 • E-mail: Ystatist@gmail.com
- Eran Goldstien’s current affiliation is Amal Group-Health Care Service, Holon, Israel.
Copyright © 2023 Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Yeungnam University Institute of Medical Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 3,429 Views
- 102 Download
Abstract
-
Background
- Poor sleep quality is associated with psychoactive substance abuse/addiction/withdrawal. Auricular acupuncture (AA) is a nonpharmacological method used for the treatment of sleep disturbances. This study aimed to examine the quality of sleep before and after AA in participants with mental and behavioral disorders due to prior multiple drug use in the therapeutic community.
-
Methods
- This was a consecutive case series of 27 participants (25 male [92.6%]). The median age was 35.0 years (interquartile range [IQR], 29.0–37.2 years), methadone/buprenorphine were not used, and the participants were treated with AA (median number of treatments, 15.0 [IQR, 12.0–18.0]) during a median period of 51.0 days (IQR, 49.0–51.0 days) according to the National Acupuncture Detoxification Association (NADA)-Acudetox protocol. Sleep quality was determined using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), a self-rated questionnaire that assesses sleep quality and disturbances over a 1-month interval.
-
Results
- The global PSQI score dropped (indicating better sleep quality) by a median of 3.0 points (IQR, 0.0–8.0 points) after treatment. In the multivariate logistic regression analysis, with an increase in global PSQI score during AA by 1 point, there was a 0.73-fold reduction in the risk of poor sleep quality post-AA (adjusted odds ratio, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.52–1.01; p<0.055; Nagelkerke's R2=0.66).
-
Conclusion
- The results revealed a positive effect of AA (by the NADA-Acudetox protocol) on sleep quality (as measured by PSQI) among participants in a treatment center with mental and behavioral disorders due to multiple drug use.
- Sleep is an active phenomenon, cyclical from a biological point of view and essential for the survival of the human race. Sleep disorders are commonly found among substance abusers, including alcohol [1], stimulants (amphetamines, cocaine, and caffeine), and opiates. Sleep disorders are common during both active substance use and detoxification [2]. In addition, there are no differences in sleep quality among mildly, moderately, and severely dependent drinkers [1].
- Both sleep disturbance and substance use disorders have been associated with negative outcomes, including decreased health-related quality of life [3], motor vehicle accidents [4], and suicide [6].
- Therefore, promoting clinical care for patients with sleep disturbances and substance use disorders has the hypothetical effect of having a cascading positive impact on recovery from substance use disorders [6,7].
- Nonpharmacological therapies to improve sleep in substance use disorders are attractive because they avoid adverse effects and the need for long-term pharmacological therapies. One nonpharmacological intervention for patients with substance use disorders is auricular acupuncture (AA). AA is an important component of traditional Chinese medicine. It has been accepted in China for thousands of years and is now used as an alternative and complementary medical therapy in Western countries. AA is one method by which specific points on the auricle are stimulated to treat various conditions [6,8,9].
- Chen et al. [10] published a systematic review of six randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and papers written in Chinese or English. They concluded that AA intervention for insomnia produces better index rates of improvement and recovery than alternative interventions. AA also produces better rates of insomnia improvement and recovery than diazepam. Compared to control interventions, AA treatment is favored by increasing nocturnal sleep up to 6 hours, with subjects feeling sufficiently refreshed upon waking [10].
- Lee et al. [11] published a systematic review of 10 RCTs performed in China, Korea, and the USA. The results suggested beneficial effects of AA on sleep efficiency compared with placebo [11]. Therefore, AA is often recommended as a treatment option for a wide spectrum of chronic conditions, such as sleep disturbances.
- Very few studies have investigated sleep quality due to AA among patients with psychoactive substance use (Table 1). This imbalance was addressed in this study.
- The objective of this study was to examine the quality of sleep before and after AA in participants with mental and behavioral disorders due to multiple drug use. The research hypothesis is that treatment with AA is associated with an improvement in the quality of sleep in this population.
Introduction
- Ethical statements: This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of AMHC (IRB No: 43Z), without requirement for informed consent because of the retrospective analysis of prospectively collected data.
- 1. Patients
- To participate in the current study, male or female patients had to meet the following inclusion criteria: (1) age 18 years and older; (2) experienced mental and behavioral disorders due to psychoactive substance use (codes F10–F19) according to the International Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th edition; (3) were in the therapeutic community Ramot Yehuda-Zoharim, Israel; (4) received AA as an integrated part of the comprehensive treatment in the community; and (5) were not treated with buprenorphine or methadone at that time. The exclusion criteria were severe metabolic or systemic disease and female participants who were pregnant or lactating.
- We analyzed prospectively collected data [12,13] in a consecutive case series (level IV evidence).
- 2. Setting
- This study was conducted in the therapeutic community Ramot Yehuda-Zoharim, Israel, which was established to treat and rehabilitate users and addicts in all areas of life, based on a broad range of different theories, treatment strategies, and methods, as well as various approaches to rehabilitation.
- Each participant was interviewed by the center’s admission committee. Each potential participant was interviewed by a doctor, social worker, and the director of admissions. The admissions committee consisted of the staff of the therapeutic community. The admissions interviews consisted of three parts. In the medical section, the medical files of the patients, illnesses, and medications were reviewed by the physician. In the social part, a psychosocial interview was conducted by the social worker to gauge the level of personal psychosocial ability of each candidate, and the mental and social support factors that generally exist in his/her life. In the final administrative part, the laws that govern life in the community were explained.
- The participants underwent extensive medical examinations and tests. Tests were performed to detect acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and tuberculosis, and a dental examination was performed to treat acute conditions as soon as possible.
- The center’s principles are based on obtaining a maximum level of independence, as well as progress in changing behaviors and previous drug-based lifestyles. The center is a laboratory of preparation for return to life that is normative in the drug-free sense. The staff has a varied background from many professions and includes previous drug users. To prevent drug use, the use of drug substitutes or any other pharmacological substances is prohibited.
- 3. Outcome measure
- The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) is a self-rated questionnaire that examines sleep quality retrospectively over a period of 1 month. Nineteen items are included in seven “component” scores: C1, subjective sleep quality; C2, sleep latency; C3, sleep duration; C4, habitual sleep efficiency; C5, sleep disturbances; C6, use of sleeping medication; and C7, daytime dysfunction. The questionnaire is easy to manage and can be completed within 5 minutes [14].
- Each component score is weighted equally on a scale from 0 (no difficulty) to 3 (severe difficulty), with higher scores representing poorer sleep quality. The seven component scores are then summed to yield a global PSQI score, which has a range of 0 to 21; higher scores indicate worse sleep quality [14]. In previous studies, the internal consistency coefficient (as measured by Cronbach alpha) ranged from 0.72 [15-17] to 0.85 [14,16,18,19], indicating a high degree of internal consistency. Cronbach alpha was used to assess the consistency of results across items in the current test.
- The internal consistency of the PSQI has not yet been investigated in populations with substance use. Nonetheless, for the Hebrew version of the PSQI, internal consistency was supported with Cronbach alpha scores from 0.52 to 0.70 in one study [17] and 0.63 in another [20].
- Poor sleep quality was defined as a global score of >5 on the PSQI [21-23], which has been determined to yield a diagnostic sensitivity of 89.6% [14] to 98.7% [19] and a specificity of 84.4% [19] to 86.5% [14] in identifying poor sleep quality vs. good sleep quality (PSQI of <5).
- 4. Interventions
- Participants were treated by acupuncturists (E.G.) according to the National Acupuncture Detoxification Association (NADA)-Acudetox protocol [6-8,24]. The protocol included the insertion of acupuncture needles into two auricles (after wiping them with alcohol). The needles were inserted at five points (sympathetic, kidney, Shen Men, liver, and lung), four to five times per week. They were left in place for 20 to 40 minutes during each treatment session. The sessions were conducted in a quiet place. Needle stimulation was performed by inserting sterilized ear acupuncture needles (type DB2, stainless steel, 15×0.18 mm; Dong Bang Acupuncture, Inc., Boryeong, Korea) to a depth of 1 to 3 mm at the appropriate points [9]. AA was the only treatment performed during the study period.
- 5. Measurement
- The Hebrew version of the PSQI [17,20-22,25] was administered before the beginning of the AA process and within 72 hours after finishing the treatment process. A clinically significant effect was defined as a decrease of at least 1.93 for a beneficial effect and an increase of 2.9 or more for a negative effect [26].
- 6. Statistical analysis
- Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS ver. 20.0 for Windows (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Categorical variables are presented as frequency tables and continuous variables as medians with interquartile ranges (IQRs). Nonparametric analysis was conducted.
- Internal consistency analysis of the seven-component PSQI score items was conducted using Cronbach alpha [27]. The pre-post comparison of the total PSQI and all components was performed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
- Univariate and multivariate (while controlling for confounding variables) logistic regression analysis was performed (with odds ratios [ORs] and 95% confidence intervals [CIs]) to establish predictors of post-AA poor sleep quality (PSQI of >5) vs. good sleep quality (PSQI of <5). Variables that were significant at the p<0.10 level in the univariate logistic regression analysis were included in the multivariate logistic regression model with post-AA sleep quality as the dependent dichotomous variable (PSQI of >5, and others) to enable evaluation of predictive performance after controlling for other variables [28,29].
- The predictive performance of these parameters was also examined using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Differences between ROC curves were identified using nonparametric comparisons of the area under the curve (AUC) [30-32]. A p-value of <0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Methods
- 1. Participants
- The sample was comprised of 27 participants. Of these participants, 25 (92.6%) were male and 14 (51.8%) were single. At the beginning of the study, the median age of the participants was 35.0 years (IQR, 29.0–37.2 years). The median length of stay (LOS) in the therapeutic community was 78.5 days (IQR, 22.0–142.0 days).
- 2. Descriptive data
- All participants had mental and behavioral disorders due to multiple drug use. All reported drug use, while only eight participants (30.8%) reported alcohol use. The median age when they began drug use was 16.0 years (IQR, 14.0–19.0 years). The median number of previous withdrawal attempts was 2 (IQR, 1.0–4.8). In the past, participants had received treatment in one to three other residential facilities and were free from psychoactive substance use during a median period of 12 months (IQR, 1.0–30.0 months).
- Participants received a median of 15 treatment sessions (IQR, 12.0–18.0 sessions) in the current study. The median period of time for treatments was 51.0 days (IQR, 49.0–51.0 days). After the AA treatments, 16 participants (59.3%) reported a positive change in how they felt, and 11 participants (40.7%) reported that they felt no change.
- 3. Outcome data
- Cronbach alpha for the global PSQI at the beginning of the follow-up period was 0.53. The median global PSQI score was 9.0 (IQR, 7.0–13.0).
- Cronbach alpha for the global PSQI at the end of the follow-up period was 0.71. The median global PSQI score was 6.0 points (IQR, 2.0–7.0 points). At the end of the follow-up period, 14 participants (51.9%) reported poor post-AA sleep quality (PSQI of >5).
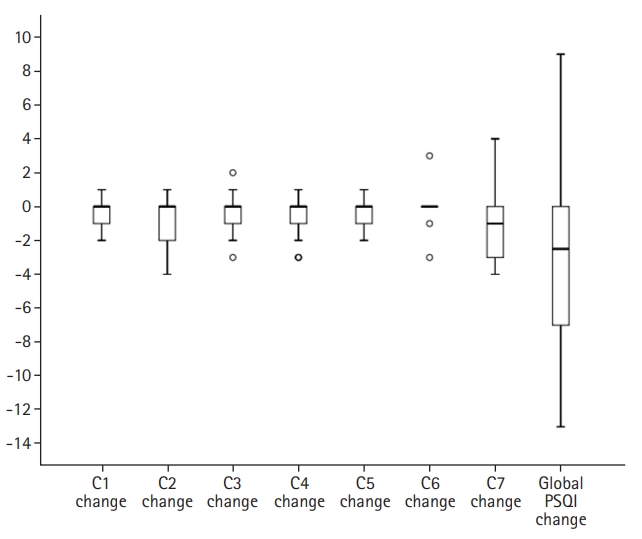
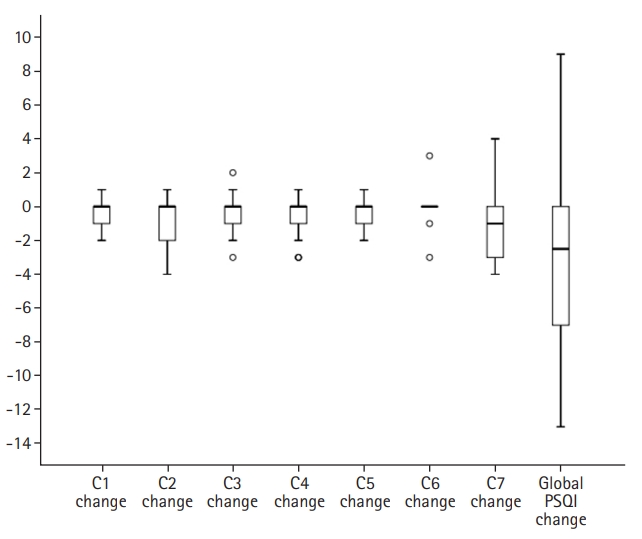
- Comparisons between PSQI components and global scores during AA treatment are presented in Table 2 and Fig. 1. From the data presented in Table 2 and Fig. 1, it can be seen that there were statistically significant reductions in subjective sleep quality (p<0.002), sleep latency (p<0.011), habitual sleep efficiency (p<0.023), sleep disturbances (p<0.007), and daytime dysfunction (p<0.015) components, as well as in global score (p<0.0001). The global score dropped (indicating better sleep quality) by a median of 3.0 points (IQR, 0.0–8.0 points) post-AA treatment.
- 4. Other analyses
- The results of the univariate logistic regression analysis are shown in Table 3. As shown in Table 3, younger age at first use (p<0.05), fewer withdrawal attempts (p<0.03), and little change in global PSQI score (p<0.02) were found to be significant predictors of poor post-AA sleep quality. The number of AA treatments was not found to be a predictor of poor sleep quality (OR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.68–1.06; p<0.15).
- The results of the multivariate logistic regression model are presented in Table 4. Only variables that significantly predicted poor sleep quality in the univariate models were chosen for multivariate analysis. With an increase in the global PSQI score during AA by 1 point, there was a 0.73-fold reduction in the risk of poor sleep quality post-AA (OR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.52–1.01; p<0.055).
- Statistical analysis of the multivariate logistic regression model (Table 4) revealed a statistically significant change from the basic model (likelihood-ratio test, 16.35; degree of freedom [df]=3; p<0.001). The explained variation in the model was high at approximately 66% (Nagelkerke R2=0.66). The Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness of fit test was not significant (χ2=5.84; df=8; p<0.67). The sensitivity and specificity of predicting post-AA poor sleep quality were 92.3% and 81.8%, respectively. The AUC-ROC of the model was 0.90 (95% CI, 0.77–1.00; p<0.001), which was considered high discrimination.
- No adverse events were observed during the follow-up period.
Results
1) Characteristics of substance use
2) Auricular acupuncture treatment
1) Global Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index at the beginning of follow-up
2) Global Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index at the end of follow-up
3) Comparison between Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index components and global scores pre- and post-auricular acupuncture
1) Univariate analysis of post-auricular acupuncture poor sleep-quality prediction
2) Multivariate analysis of post-auricular acupuncture poor sleep-quality prediction
3) Feasibility of multivariate model for post-auricular acupuncture poor sleep-quality prediction
4) Adverse events
- This study examined changes in sleep quality due to AA among participants with mental and behavioral disorders due to multiple drug use treated in a therapeutic community. The findings point to a beneficial effect of AA on sleep quality, as measured by global PSQI scores, and allowed us to accept the study hypothesis that AA treatment is associated with an improvement in the quality of sleep in psychoactive substance users. The global score pre- and post-AA treatment dropped by a median of 3.0 points, indicating that AA was clinically effective in improving sleep quality [26]. Our findings are consistent with those of previous studies, not only of pre-post cohort studies [24] but also of RCTs [6,33] and other types of studies with control subpopulations [34,35].
- In the meta-analysis, the effectiveness of AA was expressed using recovery from insomnia and improvement proportions, and the efficiency of AA (n=338) was better than that of the alternative treatments (oral estazolam [n=65], oral diazepam [n=60], barbiturates [n=60], and sham AA [n=30]) in the control population (relative risk, 1.93; 95% CI, 1.40–2.66). When the effectiveness of AA was expressed using sleep time for more than 6 hours, the effectiveness of AA (n=158) was better than that of the alternative interventions (oral estazolam [n=65], oral diazepam [n=30]) in the control population (relative risk, 2.64; 95% CI, 1.22–7.22) [10]. Another meta-analysis indicated that acupuncture and acupressure may help improve sleep-quality scores when compared to placebo (p<0.006) or no treatment (p<0.002) [36].
- A variety of possible biophysiological explanations have been proposed to understand the effect of AA on sleep quality. In traditional Chinese medicine, the insertion of needles into points on the body or ears releases qi (“life energy”) blockage. Each of the five ear points in the NADA-Acudetox protocol has a specific role. The Shen Men (“Spirit Gate”, in Chinese) point calms the emotions, and the sympathetic point balances activity in the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems and relaxes muscle tension. The lung, liver, and kidney points balance the functions of these organs. NADA-Acudetox treatment also affects the balance between yang and yin, two opposing factors that regulate functioning in living organisms in nature. NADA-Acudetox “tonifies yin,” meaning that yin elements such as softness, humidity, and darkness become stronger. This occurs at the expense of yang elements such as hardness, dryness, and lightness. Moreover, “empty fire” syndrome is treated, indicating that the feeling of inner emptiness typical of psychoactive substance misusers is replaced, during a period of treatment sessions, with a psychophysiological feeling of solidness and fullness [8].
- The western approach to acupuncture effects on the human body originates from studies (on humans and animals) focusing on the release of neurotransmitters and inhibition of pain, as well as the identification of activated areas in the human brain. AA treatment evidently affects the parasympathetic component of the autonomic nervous system and its influence on reflexes in the cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, brainstem, and spine [8].
- Moreover, previous studies have demonstrated that acupuncture increases endogenous opioid and nocturnal melatonin levels. The opioidergic system is theorized to have a somnogenic effect and may interact with melatonin to normalize the circadian cycle and promote sleep. These findings provide a possible physiological basis for how acupuncture affects sleep [11,29,37,38].
- An additional possible explanation for the positive effect of AA treatment on sleep quality is staying in the therapeutic community after the withdrawal process and, as a result, being free from the influence of multiple substances. Another rationale is the acquired personal skills of participants to adopt a new life without multiple substances in the therapeutic community.
- Participants with minimal changes in global PSQI scores were more likely to suffer from poor sleep quality than those with substantial changes. Analysis of this finding was not the aim of the current study, and there is currently no way to establish a cause-and-effect relationship between these variables.
- This study has several limitations. First, this was a consecutive case series study, as has been published in previous studies, but not in controlled trials [12,13]. Therefore, one cannot exclude that the improvement in sleep quality was due to indwelling in the therapeutic community and not specifically because of the AA treatment process. To overcome this possible uncertainty, the expected effect of time spent in the therapeutic community on sleep quality was examined. The LOS in the therapeutic community was not found to be a predictor of sleep quality. Thus, it can be concluded that staying in a therapeutic community is unlikely to improve sleep quality among subjects with mental and behavioral disorders due to multiple drug use.
- Second, the effect of AA on sleep quality was not examined after an equal number of AA treatments. To overcome this bias, we examined the expected effect of the number of AA treatments on sleep quality. The number of AA treatments was not found to be a predictor of sleep quality. From this, it can be concluded that cumulative exposure to AA-treatment processes only likely does not improve sleep quality in this subpopulation.
- Third, middle- and/or long-term outcomes may be more meaningful and helpful in providing patients with mental and behavioral disorders due to multiple drug use.
- Fourth, logistic regression models, based on small study populations, may have limited power. However, each of the parameters mentioned above in the multivariate model, alone and together, indicated that the multivariate logistic regression model was accurate for post-AA poor sleep quality prediction.
- Finally, the participants in our study had mental and behavioral disorders due to multiple drug use. Because of the retrospective design of the study, there was no way to determine the different types of substances used pre-AA and, therefore, to establish the influence of each substance on changes in sleep quality.
- With minimal utilization of high-cost equipment, AA can be included in integrated care for sleep-quality improvement. In our study, the results revealed a positive effect of AA (by the NADA-Acudetox protocol) on sleep quality (as measured by PSQI) among participants, who are in a therapeutic community, with mental and behavioral disorders due to multiple drug use. Future prospective designs need to be more specific in methodology, such as implementation, protocol selection, extension, and time of AA stimulation in participants exposed to different substances. We expect that this study will raise attention to this low-cost, safe interventional method and produce scientific evidence to support its application in populations with mental and behavioral disorders due to multiple drug use.
Discussion
-
Conflicts of interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
Funding
None.
-
Author contributions
Conceptualization, Data curation: YG, EG; Formal analysis, Project administration, Supervision: EG; Methodology, Investigation, Software: YG; Writing-original draft: YG; Writing-review & editing: YG, EG.
Notes
| Study | Year | Study and duration | Participant | Intervention | Control | PSQI outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jiang et al. [33] | 2010 | Single-blinded, RCT, 4 weeks | People with insomnia | AA (n=63) | AA on sham points (n=62) | As compared to control population, AA improved the quantity and quality of sleep |
| Jiao et al. [34] | 2015 | A three-factor (3 needling protocols) and three-level experimental scheme, based on orthogonal method | Patients of insomnia differentiated as internal harassment of phlegm-heat syndrome (n=54) | AA | Body acupuncture and abdominal acupuncture | AA, after body acupuncture, is the second best choice for insomnia |
| King et al. [35] | 2015 | A feasibility 3-week study | Veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder and sleep disturbance | Multimodal treatment +9 AA treatments (n=12) | Multimodal treatment without AA (n=8) | Differences between groups were found on sleep quality (p<0.003) and daytime dysfunction (p<0.004) components |
| Current study | 2022 | Consecutive case series study, median period of 7.3 weeks | Patients with mental and behavioral disorders due to multiple drug use in therapeutic community | AA according to NADA-Acudetox protocol (n=27) | No | PSQI global score declined by median of 3.0 points (p<0.0001) |
| Variable | OR (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| Age at first use (yr) | 0.76 (0.48–1.20) | 0.240 |
| Withdrawal attempts | 0.59 (0.30–1.15) | 0.120 |
| Global PSQI score change (point) | 0.73 (0.52–1.01) | 0.055 |
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; PSQI, Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index.
For the multivariate logistic regression model, Nagelkerke R2=0.66; sensitivity=92.3%; specificity=81.8%; likelihood-ratio test=16.35; degree of freedom (df)=3; p<0.001; Hosmer–Lemeshow test, χ2=5.84; df=8; p<0.67; area under the receiver operating characteristic curve=0.90 (95% CI, 0.77–1.00), p<0.001.
- 1. Foster JH, Peters TJ. Impaired sleep in alcohol misusers and dependent alcoholics and the impact upon outcome. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 1999;23:1044–51.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, Ruiz P. Kaplan & Sadock’s synopsis of psychiatry: behavioral sciences/clinical psychiatry. 11th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.
- 3. Kyle SD, Morgan K, Espie CA. Insomnia and health-related quality of life. Sleep Med Rev 2010;14:69–82.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Callaghan RC, Gatley JM, Veldhuizen S, Lev-Ran S, Mann R, Asbridge M. Alcohol- or drug-use disorders and motor vehicle accident mortality: a retrospective cohort study. Accid Anal Prev 2013;53:149–55.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Bernert RA, Kim JS, Iwata NG, Perlis ML. Sleep disturbances as an evidence-based suicide risk factor. Curr Psychiatry Rep 2015;17:554.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 6. Berman AH, Lundberg U, Krook AL, Gyllenhammar C. Treating drug using prison inmates with auricular acupuncture: a randomized controlled trial. J Subst Abuse Treat 2004;26:95–102.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Ahlberg R, Skårberg K, Brus O, Kjellin L. Auricular acupuncture for substance use: a randomized controlled trial of effects on anxiety, sleep, drug use and use of addiction treatment services. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy 2016;11:24.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Berman AH. Auricular acupuncture as an adjunct to treating substance use disorder. Dir Addict Treat Prev 2006;10:25–44.PDF
- 9. Gimelfarb Y, Goldstein E, Natan Z, Elwahidi S, Kaikov E, Baruch Y. Randomized controlled pilot trial of auricular acupuncture in men with schizophrenia and co-occurring multisubstance use disorders. Heroin Addict Relat Clin Probl 2016;18:29–36.
- 10. Chen HY, Shi Y, Ng CS, Chan SM, Yung KK, Zhang QL. Auricular acupuncture treatment for insomnia: a systematic review. J Altern Complement Med 2007;13:669–76.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Lee MS, Shin BC, Suen LK, Park TY, Ernst E. Auricular acupuncture for insomnia: a systematic review. Int J Clin Pract 2008;62:1744–52.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Wu Y, Zou C, Liu X, Wu X, Lin Q. Auricular acupressure helps improve sleep quality for severe insomnia in maintenance hemodialysis patients: a pilot study. J Altern Complement Med 2014;20:356–63.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Luo M, Qu X, Li S, Zhao J, Zhao Y, Jiao Y, et al. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation for primary insomnia and affective disorder:a report of 35 cases. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 2017;37:269–73.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF 3rd, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res 1989;28:193–213.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Doi Y, Minowa M, Uchiyama M, Okawa M, Kim K, Shibui K, et al. Psychometric assessment of subjective sleep quality using the Japanese version of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI-J) in psychiatric disordered and control subjects. Psychiatry Res 2000;97:165–72.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Beck SL, Schwartz AL, Towsley G, Dudley W, Barsevick A. Psychometric evaluation of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index in cancer patients. J Pain Symptom Manage 2004;27:140–8.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Shochat T, Tzischinsky O, Oksenberg A, Peled R. Validation of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index Hebrew translation (PSQI-H) in a sleep clinic sample. Isr Med Assoc J 2007;9:853–6.PubMed
- 18. Carpenter JS, Andrykowski MA. Psychometric evaluation of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. J Psychosom Res 1998;45:5–13.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Backhaus J, Junghanns K, Broocks A, Riemann D, Hohagen F. Test-retest reliability and validity of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index in primary insomnia. J Psychosom Res 2002;53:737–40.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Handelzalts JE, Hairston IS, Matatyahu A. Construct validity and psychometric properties of the Hebrew version of the City Birth Trauma Scale. Front Psychol 2018;9:1726.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Palmieri PA, Chipman KJ, Canetti D, Johnson RJ, Hobfoll SE. Prevalence and correlates of sleep problems in adult Israeli Jews exposed to actual or threatened terrorist or rocket attacks. J Clin Sleep Med 2010;6:557–64.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Orbach-Zinger S, Fireman S, Ben-Haroush A, Karoush T, Klein Z, Mazarib N, et al. Preoperative sleep quality predicts postoperative pain after planned caesarean delivery. Eur J Pain 2017;21:787–94.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. Zhao D, Wang H, Feng X, Lv G, Li P. Relationship between neuroticism and sleep quality among asthma patients: the mediation effect of mindfulness. Sleep Breath 2019;23:925–31.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. Cronin C, Conboy L. Using the NADA protocol to treat combat stress-induced insomnia: a pilot study. J Chin Med 2013;103:50–6.
- 25. Schreiber S, Dolberg OT, Barkai G, Peles E, Leor A, Rapoport E, et al. Primary intervention for memory structuring and meaning acquisition (PIMSMA): study of a mental health first-aid intervention in the ED with injured survivors of suicide bombing attacks. Am J Disaster Med 2007;2:307–20.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 26. Yaoying L, Yan L, Jiyang P, Darong W. Research about the minimal important difference of Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index based on clinical trials of TCM. J Guangzhou Univ Tradit Chin Med 2013;30:574–8.
- 27. Cronbach LJ. Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika 1951;16:297–334.ArticlePDF
- 28. Field A. Logistic regression. In: Field A. Discovering statistics using SPSS for Windows: advanced techniques for the beginner. London: SAGE Publication; 2000. p. 163–204.
- 29. Hanley JA, McNeil BJ. A method of comparing the areas under receiver operating characteristic curves derived from the same cases. Radiology 1983;148:839–43.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Hosmer DW Jr, Lemeshow S, Sturdivant RX. Applied logistic regression. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 2013.
- 31. Metz CE. Basic principles of ROC analysis. Semin Nucl Med 1978;8:283–98.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Zou KH, O’Malley AJ, Mauri L. Receiver-operating characteristic analysis for evaluating diagnostic tests and predictive models. Circulation 2007;115:654–7.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Jiang B, Ma ZH, Zuo F. Auricular acupuncture for insomnia:a randomized controlled trial. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2010;31:1400–2.PubMed
- 34. Jiao Y, Han Y, Li X, Fang YG, Liu ZH, Zhou WN, et al. Comparison of body, auricular, and abdominal acupuncture treatments for insomnia differentiated as internal harassment of phlegm-heat syndrome: an orthogonal design. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015;2015:578972.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 35. King HC, Spence DL, Hickey AH, Sargent P, Elesh R, Connelly CD. Auricular acupuncture for sleep disturbance in veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder: a feasibility study. Mil Med 2015;180:582–90.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Cheuk DK, Yeung WF, Chung KF, Wong V. Acupuncture for insomnia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007;(3):CD005472.Article
- 37. Spence DW, Kayumov L, Chen A, Lowe A, Jain U, Katzman MA, et al. Acupuncture increases nocturnal melatonin secretion and reduces insomnia and anxiety: a preliminary report. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 2004;16:19–28.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Roth T, Roehrs T, Pies R. Insomnia: pathophysiology and implications for treatment. Sleep Med Rev 2007;11:71–9.ArticlePubMed
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations


 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite