Indexed in: ESCI, Scopus, PubMed,
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
FREE article processing charge

Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
Editorial
- Understanding sleep and sleep disturbances in autism spectrum disorder, and management of insomnia: an update
- Hye-Geum Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):265-266. Published online September 13, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2021.01459
- 2,814 View
- 82 Download
Focused Review articles
- Understanding insomnia as systemic disease
- Seokho Yun, Sohye Jo
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):267-274. Published online September 13, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2021.01424
- 5,427 View
- 117 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Sleep plays a critical role in homeostasis of the body and mind. Insomnia is a disease that causes disturbances in the initiation and maintenance of sleep. Insomnia is known to affect not only the sleep process itself but also an individual’s cognitive function and emotional regulation during the daytime. It increases the risk of various neuropsychiatric diseases such as depression, anxiety disorder, and dementia. Although it might appear that insomnia only affects the nervous system, it is also a systemic disease that affects several aspects of the body, such as the cardiovascular, endocrine, and immune systems; therefore, it increases the risk of various diseases such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and infection. Insomnia has a wide range of effects on our bodies because sleep is a complex and active process. However, a high proportion of patients with insomnia do not seek treatment, which results in high direct and indirect costs. This is attributed to the disregard of many of the negative effects of insomnia. Therefore, we expect that understanding insomnia as a systemic disease will provide an opportunity to understand the condition better and help prevent secondary impairment due to insomnia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Medical service utilization patterns among adults with insomnia: A retrospective cohort study
Min Kyung Hyun, Jang Won Lee
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2024; 67: 102325. CrossRef - Socio-Ecological Context of Sleep: Gender Differences and Couples’ Relationships as Exemplars
Andrea N. Decker, Alexandra R. Fischer, Heather E. Gunn
Current Psychiatry Reports.2022; 24(12): 831. CrossRef - Clinical Spectrum and Trajectory of Innovative Therapeutic Interventions for Insomnia: A Perspective
Yun-Jo Lo, Viraj Krishna Mishra, Hung-Yao Lo, Navneet Kumar Dubey, Wen-Cheng Lo
Aging and disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding sleep and sleep disturbances in autism spectrum disorder, and management of insomnia: an update
Hye-Geum Kim
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2021; 38(4): 265. CrossRef
- Medical service utilization patterns among adults with insomnia: A retrospective cohort study
- An update on the cause and treatment of sleep disturbance in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder
- Wan Seok Seo
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):275-281. Published online September 13, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2021.01410
- 5,729 View
- 180 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by abnormalities in social communication/interaction and restrictive, repetitive patterns of behavior. ASD is a relatively common psychiatric disorder, with a prevalence of approximately 1.7% in children. Although many children and adolescents with ASD visit the hospital for medical help for emotional and behavioral problems such as mood instability and self-harming behavior, there are also many visits for sleep disturbances such as insomnia and sleep resistance. Sleep disturbances are likely to increase fatigue and daytime sleepiness, impaired concentration, negatively impact on daytime functioning, and pose challenges in controlling anger and aggressive behavior. Sleep disturbance in children and adolescents with ASD negatively affects the quality of life, nothing to say the quality of life of their families and school members. In this review, sleep disturbances that are common in children and adolescents with ASD and adolescents are presented. The developmental and behavioral impacts of sleep disturbances in ASD were also considered. Finally, non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatments for sleep disturbances in children and adolescents with ASD and adolescents are reviewed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current Pharmacological Treatment for Sleep Disorders in Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Hatice Altun, Semiha Cömertoğlu Arslan
European Journal of Therapeutics.2024; 30(2): 227. CrossRef - Forensic psychiatric assessment in autism spectrum disorder: Experience of a forensic psychiatry inpatient clinic from Türkiye
Muhammed Emin Boylu, İlker Taşdemir, Mehmet Doğan, Tuba Özcanlı
Journal of Forensic Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sleep and Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Comprehensive Review of Diagnosis, Markers, Interventions, and Treatments
Deepa Burman, Karthikeyan Ramanujam, Dilshad Manzar, Vijay Kumar Chattu, David Warren Spence, Nevin F. W. Zaki, Haitham Jahrami, Seithikurippu R. Pandi-Perumal
Sleep and Vigilance.2023; 7(1): 9. CrossRef - Efficacy of Melatonin for Insomnia in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Meta-analysis
Mei Xiong, Fang Li, Zhaohua Liu, Xin Xie, Hongli Shen, Weiteng Li, Liping Wei, Rongfang He
Neuropediatrics.2023; 54(03): 167. CrossRef - Sleep disturbances and emotional dysregulation in young children with autism spectrum, intellectual disability, or global developmental delay
Irene Favole, Chiara Davico, Daniele Marcotulli, Roberta Sodero, Barbara Svevi, Federico Amianto, Federica S. Ricci, G. Maurizio Arduino, Benedetto Vitiello
Sleep Medicine.2023; 105: 45. CrossRef - Where I am from matters: factors influencing behavioral and emotional changes in autistic individuals during COVID-19 in Latin America
María Cecilia Montenegro, Ana C. Ramírez, Juventino Hernandez Rodriguez, Bianca T. Villalobos, Gabriela Garrido, Cecilia Amigo, Daniel Valdez, Natalia Barrios, Sebastián Cukier, Alexia Rattazzi, Analía Rosoli, Ricardo García, Cristiane S. Paula, Georgina
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A novel case of prolonged Ifosfamide encephalopathy and long-term treatment with methylene blue: a case report and review of literature
Gabriel Chain, Mudit Kalia, Karen Kestenbaum, Lara Pappas, Anna Sechser-Perl, Gadi Abebe Campino, Nibal Zaghloul
BMC Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Sleep Disturbances in Children Affected by Autism Spectrum Disorder
Jessica Galli, Erika Loi, Lucrezia Maria Visconti, Paola Mattei, Anna Eusebi, Stefano Calza, Elisa Fazzi
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of sleep problem in children aged 1–3 years with autism spectrum disorder in Zhejiang province, China
Dan Yao, Shasha Wang, Fangfang Li, Minjie Gao, Jie Shao
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding sleep and sleep disturbances in autism spectrum disorder, and management of insomnia: an update
Hye-Geum Kim
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2021; 38(4): 265. CrossRef
- Current Pharmacological Treatment for Sleep Disorders in Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Effects and mechanisms of a mindfulness-based intervention on insomnia
- Hye-Geum Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):282-288. Published online January 14, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00850
- 40,098 View
- 173 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Medication alone is not sufficient to treat insomnia. In addition, the side effects of sleep medications themselves cannot be ignored during treatment. Insomnia begins with poor sleep quality and discomfort, but as it continues, patients fall into a vicious circle of insomnia with negative thoughts and dysfunctional and distorted perceptions related to sleep. Mindfulness-based intervention for insomnia corrects these sequential cognitive and behavioral processes. The mindfulness technique basically recognizes all the thoughts, feelings, and experiences that occur to us as they are, nonjudgmentally, and then trains them to return to the senses of our body. In this way, while noticing all the processes of the sequential vicious cycle and training them to return to our bodies (e.g., breathing), mindfulness determines whether we are really sleepy or just fatigued. This mindfulness-based intervention can be a useful nonpharmaceutical intervention for insomnia, and its stability and efficacy has been proven by many studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative efficacy and acceptability of interventions for insomnia in breast cancer patients: A protocol for systematic review and network meta-analysis
Zhifan Li, Qian Wang, Junxia Xu, Qihua Song, Xiaoling Ling, Ya Gao, Junqiang Lei, Andrea Giannini
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(3): e0282614. CrossRef - Cognitive and Somatic Mediators of the Effects of Trait Mindfulness on Mental Health Adjustment Following Bereavement
Mariel Emrich, Crystal L. Park, Adam B. David, Lucy Finkelstein-Fox
Mindfulness.2023; 14(12): 2932. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a 4-Day Mindfulness-Based Intervention in a 2-Month Follow-Up for Chinese Incarcerated People
Jieting Zhang, Zening Zheng, Lina Wang, Christina M. Luberto, Man (Sophie) Zhang, Yuhua Wen, Qi Su, Can Jiao
Behavior Therapy.2022; 53(5): 981. CrossRef - Understanding sleep and sleep disturbances in autism spectrum disorder, and management of insomnia: an update
Hye-Geum Kim
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2021; 38(4): 265. CrossRef - Effects of mindful breathing combined with sleep-inducing exercises in patients with insomnia
Hui Su, Li Xiao, Yue Ren, Hui Xie, Xiang-Hong Sun
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(29): 8740. CrossRef
- Comparative efficacy and acceptability of interventions for insomnia in breast cancer patients: A protocol for systematic review and network meta-analysis
Review articles
- Avulsion injuries: an update on radiologic findings
- Changwon Choi, Sun Joo Lee, Hye Jung Choo, In Sook Lee, Sung Kwan Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):289-307. Published online August 13, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2021.01102
- 10,119 View
- 205 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
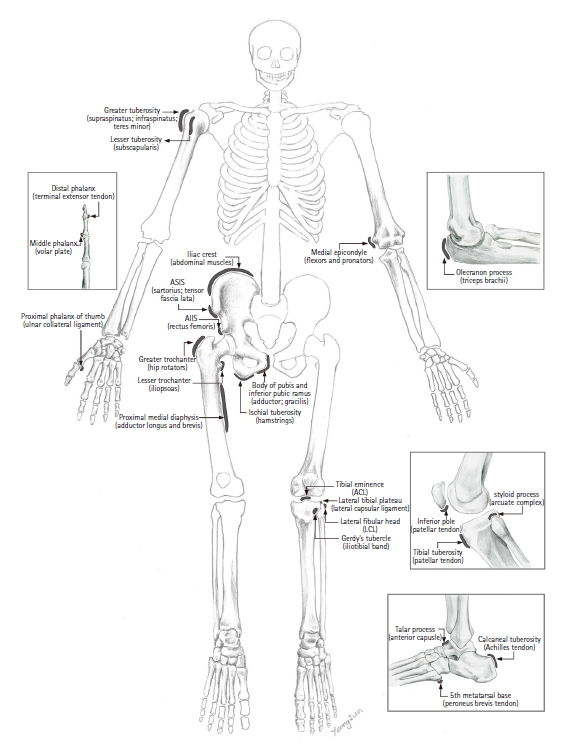
PDF - Avulsion injuries result from the application of a tensile force to a musculoskeletal unit or ligament. Although injuries tend to occur more commonly in skeletally immature populations due to the weakness of their apophysis, adults may also be subject to avulsion fractures, particularly those with osteoporotic bones. The most common sites of avulsion injuries in adolescents and children are apophyses of the pelvis and knee. In adults, avulsion injuries commonly occur within the tendon due to underlying degeneration or tendinosis. However, any location can be involved in avulsion injuries. Radiography is the first imaging modality to diagnose avulsion injury, although advanced imaging modalities are occasionally required to identify subtle lesions or to fully delineate the extent of the injury. Ultrasonography has a high spatial resolution with a dynamic assessment potential and allows the comparison of a bone avulsion with the opposite side. Computed tomography is more sensitive for depicting a tiny osseous fragment located adjacent to the expected attachment site of a ligament, tendon, or capsule. Moreover, magnetic resonance imaging is the best imaging modality for the evaluation of soft tissue abnormalities, especially the affected muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Acute avulsion injuries usually manifest as avulsed bone fragments. In contrast, chronic injuries can easily mimic other disease processes, such as infections or neoplasms. Therefore, recognizing the vulnerable sites and characteristic imaging features of avulsion fractures would be helpful in ensuring accurate diagnosis and appropriate patient management. To this end, familiarity with musculoskeletal anatomy and mechanism of injury is necessary.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical management of posterior ligament complex stripping in an adolescent spinal flexion distraction injury: A case report and literature review
Dong-Ju Lim
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2024; 114: 109195. CrossRef - Ischial Tuberosity Avulsion Fracture Mimicking Calcified Mass on Plain Films: A Case Report
Mason A Williams, Lena Naffaa
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - ESR essentials: MRI of the knee—practice recommendations by ESSR
Anagha P. Parkar, Miraude E. A. P. M. Adriaensen
European Radiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Isolated fracture of the lesser tuberosity of the humerus – a rare injury that requires surgical treatment
Miodrag Glisic, Vladan Stevanovic, Aleksandar Jevtic, Uros Jovicevic, Ivan Jankovic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2023; 80(3): 279. CrossRef
- Surgical management of posterior ligament complex stripping in an adolescent spinal flexion distraction injury: A case report and literature review
- An update on immunotherapy with PD-1 and PD-L1 blockade
- Sung Ae Koh
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):308-317. Published online September 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2021.01312
- 4,469 View
- 95 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
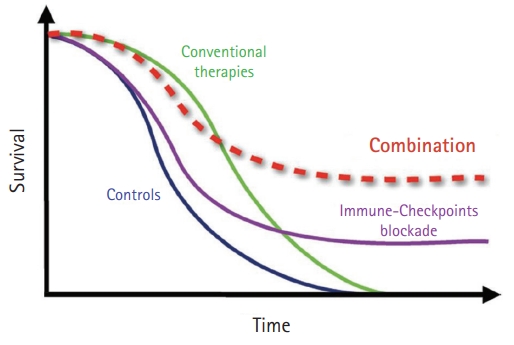
PDF - Cancer is the leading cause of death and is on the rise worldwide. Until 2010, the development of targeted treatment was mainly focused on the growth mechanisms of cancer. Since then, drugs with mechanisms related to tumor immunity, especially immune checkpoint inhibitors, have proven effective, and most pharmaceutical companies are striving to develop related drugs. Programmed cell death-1 and programmed cell death ligand-1 inhibitors have shown great success in various cancer types. They showed durable and sustainable responses and were approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. However, the response to inhibitors showed low percentages of cancer patients; 15% to 20%. Therefore, combination strategies with immunotherapy and conventional treatments were used to overcome the low response rate. Studies on combination therapy have typically reported improvements in the response rate and efficacy in several cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and urogenital cancers. The combination of chemotherapy or targeted agents with immunotherapy is one of the leading pathways for cancer treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Immune checkpoint inhibitors associated cardiovascular immune-related adverse events
Wonyoung Jo, Taejoon Won, Abdel Daoud, Daniela Čiháková
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Therapeutic targeting of thioredoxin reductase 1 causes ferroptosis while potentiating anti-PD-1 efficacy in head and neck cancer
Ming-Shou Hsieh, Hang Huong Ling, Syahru Agung Setiawan, Mardiah Suci Hardianti, Iat-Hang Fong, Chi-Tai Yeh, Jia-Hong Chen
Chemico-Biological Interactions.2024; 395: 111004. CrossRef
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors associated cardiovascular immune-related adverse events
Original articles
- Usefulness of presepsin in predicting the prognosis of patients with sepsis or septic shock: a retrospective cohort study
- Jeong Suk Koh, Yoon Joo Kim, Da Hyun Kang, Jeong Eun Lee, Song-I Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):318-325. Published online June 15, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2021.01018
- 5,759 View
- 135 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The diagnosis and prediction of prognosis are important in patients with sepsis, and presepsin is helpful. In this study, we aimed to examine the usefulness of presepsin in predicting the prognosis of sepsis in Korea.
Methods
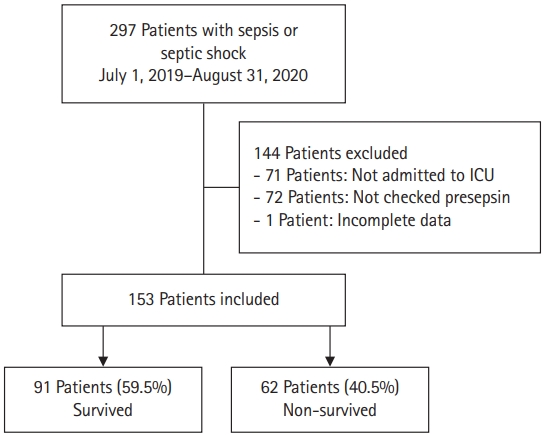
Patients diagnosed with sepsis according to the sepsis-3 criteria were recruited into the study and classified into surviving and non-surviving groups based on in-hospital mortality. A total of 153 patients (33 and 121 patients with sepsis and septic shock, respectively) were included from July 2019 to August 2020.
Results
Among the 153 patients with sepsis, 91 and 62 were in the survivor and non-survivor groups, respectively. Presepsin (p=0.004) and lactate (p=0.003) levels and the sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) scores (p<0.001) were higher in the non-survivor group. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis revealed poor performances of presepsin and lactate in predicting the prognosis of sepsis (presepsin: area under the curve [AUC]=0.656, p=0.001; lactate: AUC=0.646, p=0.003). The SOFA score showed the best performance, with the highest AUC value (AUC=0.751, p<0.001). The prognostic cutoff point for presepsin was 1,176 pg/mL. Presepsin levels of >1,176 pg/mL (odds ratio [OR], 3.352; p<0.001), lactate levels (OR, 1.203; p=0.003), and SOFA score (OR, 1.249; p<0.001) were risk factors for in-hospital mortality.
Conclusion
Presepsin levels were higher in non-survivors than in survivors. Thus, presepsin may be a valuable biomarker in predicting the prognosis of sepsis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Free Radical–Associated Gene Signature Predicts Survival in Sepsis Patients
Anlin Feng, Marissa D. Pokharel, Ying Liang, Wenli Ma, Saurabh Aggarwal, Stephen M. Black, Ting Wang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(8): 4574. CrossRef - Presepsin in Critical Illness: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives
Paolo Formenti, Miriam Gotti, Francesca Palmieri, Stefano Pastori, Vincenzo Roccaforte, Alessandro Menozzi, Andrea Galimberti, Michele Umbrello, Giovanni Sabbatini, Angelo Pezzi
Diagnostics.2024; 14(12): 1311. CrossRef - Diagnostic and Prognostic Roles of C-Reactive Protein, Procalcitonin, and Presepsin in Acute Kidney Injury Patients Initiating Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
Suyeon Han, Moo-Jun Kim, Ho-Joon Ko, Eu-Jin Lee, Hae-Ri Kim, Jae-Wan Jeon, Young-Rok Ham, Ki-Ryang Na, Kang-Wook Lee, Song-I. Lee, Dae-Eun Choi, Heyrim Park
Diagnostics.2023; 13(4): 777. CrossRef - Existe Relação entre Miocardite Aguda e a Permeabilidade Intestinal? Dois Biomarcadores nos Ajudam a Responder a esta Pergunta
Fernando Arturo Effio Solis, Adriana Brentegani, Marcelo Luiz Campos Vieira
Arquivos Brasileiros de Cardiologia.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Biomarkers in sepsis-looking for the Holy Grail or chasing a mirage!
Neelmani Ahuja, Anjali Mishra, Ruchi Gupta, Sumit Ray
World Journal of Critical Care Medicine.2023; 12(4): 188. CrossRef - Presepsin as a Novel Biomarker in predicting In‐hospital Mortality in Patients With COVID‐19 Pneumonia
Hebatallah Hany Assal, Safaa Mohamed Abdelrahman, Maha AlyAlden Abdelbasset, Mai Abdelaziz, Irene Mohamed Sabry, Marwa Moawad Shaban
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2022; 118: 155. CrossRef
- Free Radical–Associated Gene Signature Predicts Survival in Sepsis Patients
- Sulfatase 1 and sulfatase 2 as novel regulators of macrophage antigen presentation and phagocytosis
- Hyun-Je Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Young-Hoon Hong
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):326-336. Published online June 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2021.01025

- 4,854 View
- 85 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Sulfation of heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) is critical for the binding and signaling of ligands that mediate inflammation. Extracellular 6-O-endosulfatases regulate posttranslational sulfation levels and patterns of HSPGs. In this study, extracellular 6-O-endosulfatases, sulfatase (Sulf)-1 and Sulf-2, were evaluated for their expression and function in inflammatory cells and tissues.
Methods
Harvested human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were treated with phytohemagglutinin and lipopolysaccharide, and murine peritoneal macrophages were stimulated with interleukin (IL)-1β for the evaluation of Sulf-1 and Sulf-2 expression. Sulf expression in inflammatory cells was examined in the human rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovium by immunofluorescence staining. The antigen presentation and phagocytic activities of macrophages were compared according to the expression state of Sulfs. Sulfs-knockdown macrophages and Sulfs-overexpressing macrophages were generated using small interfering RNAs and pcDNA3.1 plasmids for Sulf-1 and Sulf-2, respectively.
Results
Lymphocytes and monocytes showed weak Sulf expression, which remained unaffected by IL-1β. However, peritoneal macrophages showed increased expression of Sulfs upon stimulation with IL-1β. In human RA synovium, two-colored double immunofluorescent staining of Sulfs and CD68 revealed active upregulation of Sulfs in macrophages of inflamed tissues, but not in lymphocytes of lymphoid follicles. Macrophages are professional antigen-presenting cells. The antigen presentation and phagocytic activities of macrophages were dependent on the level of Sulf expression, suppressed in Sulfs-knockdown macrophages, and enhanced in Sulfs-overexpressing macrophages.
Conclusion
The results demonstrate that upregulation of Sulfs in macrophages occurs in response to inflammation, and Sulfs actively regulate the antigen presentation and phagocytic activities of macrophages as novel immune regulators. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 6-O-endosulfatases in tumor metastasis: heparan sulfate proteoglycans modification and potential therapeutic targets
Mengzhen Han
American Journal of Cancer Research.2024; 14(2): 897. CrossRef - The prognostic value and immunological role of SULF2 in adrenocortical carcinoma
Jiusong Yan, Xiaodu Xie, Qinke Li, Peihe Liang, Junyong Zhang, Guangyong Xu
Heliyon.2023; 9(2): e13613. CrossRef - Machine learning-based metabolism-related genes signature, single-cell RNA sequencing, and experimental validation in hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Jie He, Bo Wang, Meifeng Chen, Lingmeng Song, Hezhi Li
Medicine.2023; 102(40): e34940. CrossRef - Extracellular sulfatase-2 is overexpressed in rheumatoid arthritis and mediates the TNF-α-induced inflammatory activation of synovial fibroblasts
Ruby J. Siegel, Anil K. Singh, Paul M. Panipinto, Farheen S. Shaikh, Judy Vinh, Sang U. Han, H. Mark Kenney, Edward M. Schwarz, Cynthia S. Crowson, Sadik A. Khuder, Basil S. Khuder, David A. Fox, Salahuddin Ahmed
Cellular & Molecular Immunology.2022; 19(10): 1185. CrossRef - Heparan Sulfate Glycosaminoglycan Is Predicted to Stabilize Inflammatory Infiltrate Formation and RANKL/OPG Ratio in Severe Periodontitis in Humans
Roko Duplancic, Marija Roguljic, Darko Bozic, Darko Kero
Bioengineering.2022; 9(10): 566. CrossRef - Mood Regulatory Actions of Active and Sham Nucleus Accumbens Deep Brain Stimulation in Antidepressant Resistant Rats
Rajas P. Kale, Thanh Thanh L. Nguyen, J. Blair Price, Nathanael J. Yates, Ken Walder, Michael Berk, Roy V. Sillitoe, Abbas Z. Kouzani, Susannah J. Tye
Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- 6-O-endosulfatases in tumor metastasis: heparan sulfate proteoglycans modification and potential therapeutic targets
- Prognostic impact of chromogranin A in patients with acute heart failure
- Hong Nyun Kim, Dong Heon Yang, Bo Eun Park, Yoon Jung Park, Hyeon Jeong Kim, Se Yong Jang, Myung Hwan Bae, Jang Hoon Lee, Hun Sik Park, Yongkeun Cho, Shung Chull Chae
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):337-343. Published online July 8, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00843

- 4,317 View
- 76 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Chromogranin A (CgA) levels have been reported to predict mortality in patients with heart failure. However, information on the prognostic value and clinical availability of CgA is limited. We compared the prognostic value of CgA to that of previously proven natriuretic peptide biomarkers in patients with acute heart failure.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated 272 patients (mean age, 68.5±15.6 years; 62.9% male) who underwent CgA test in the acute stage of heart failure hospitalization between June 2017 and June 2018. The median follow-up period was 348 days. Prognosis was assessed using the composite events of 1-year death and heart failure hospitalization.
Results
In-hospital mortality rate during index admission was 7.0% (n=19). During the 1-year follow-up, a composite event rate was observed in 12.1% (n=33) of the patients. The areas under the receiver-operating characteristic curves for predicting 1-year adverse events were 0.737 and 0.697 for N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and CgA, respectively. During follow-up, patients with high CgA levels (>158 pmol/L) had worse outcomes than those with low CgA levels (≤158 pmol/L) (85.2% vs. 58.6%, p<0.001). When stratifying the patients into four subgroups based on CgA and NT-proBNP levels, patients with high NT-proBNP and high CgA had the worst outcome. CgA had an incremental prognostic value when added to the combination of NT-proBNP and clinically relevant risk factors.
Conclusion
The prognostic power of CgA was comparable to that of NT-proBNP in patients with acute heart failure. The combination of CgA and NT-proBNP can improve prognosis prediction in these patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Congestion Biomarkers in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction
Michele Correale, Francesco Fioretti, Lucia Tricarico, Francesca Croella, Natale Daniele Brunetti, Riccardo M. Inciardi, Anna Vittoria Mattioli, Savina Nodari
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(11): 3834. CrossRef - Novel Biomarkers of Renal Dysfunction and Congestion in Heart Failure
Agata Zdanowicz, Szymon Urban, Barbara Ponikowska, Gracjan Iwanek, Robert Zymliński, Piotr Ponikowski, Jan Biegus
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(6): 898. CrossRef
- The Role of Congestion Biomarkers in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction
- Treatment decision for cancer patients with fever during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic
- In Hee Lee, Sung Ae Koh, Soo Jung Lee, Sun Ah Lee, Yoon Young Cho, Ji Yeon Lee, Jin Young Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):344-349. Published online August 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2021.01144
- 4,771 View
- 58 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Cancer patients have been disproportionally affected by the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, with high rates of severe outcomes and mortality. Fever is the most common symptom in COVID-19 patients. During the COVID-19 pandemic, physicians may have difficulty in determining the cause of fever (COVID-19, another infection, or cancer fever) in cancer patients. Furthermore, there are no specific guidelines for managing cancer patients with fever during the COVID-19 pandemic. Thus, this study evaluated the clinical characteristics and outcomes of cancer patients with fever during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
This study retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 328 cancer patients with COVID-19 symptoms (fever) admitted to five hospitals in Daegu, Korea from January to October 2020. We obtained data on demographics, clinical manifestations, laboratory test results, chest computed tomography images, cancer history, cancer treatment, and outcomes of all enrolled patients from electronic medical records.
Results
The most common COVID-19-like symptoms were fever (n=256, 78%). Among 256 patients with fever, only three (1.2%) were diagnosed with COVID-19. Most patients (253, 98.8%) with fever were not diagnosed with COVID-19. The most common solid malignancies were lung cancer (65, 19.8%) and hepatobiliary cancer (61, 18.6%). Twenty patients with fever experienced a delay in receiving cancer treatment. Eighteen patients discontinued active cancer treatment because of fever. Major events during the treatment delay period included death (2.7%), cancer progression (1.5%), and major organ dysfunction (2.7%).
Conclusion
Considering that only 0.9% of patients tested for COVID-19 were positive, screening for COVID-19 in cancer patients with fever should be based on the physician’s clinical decision, and patients might not be routinely tested.
Case reports
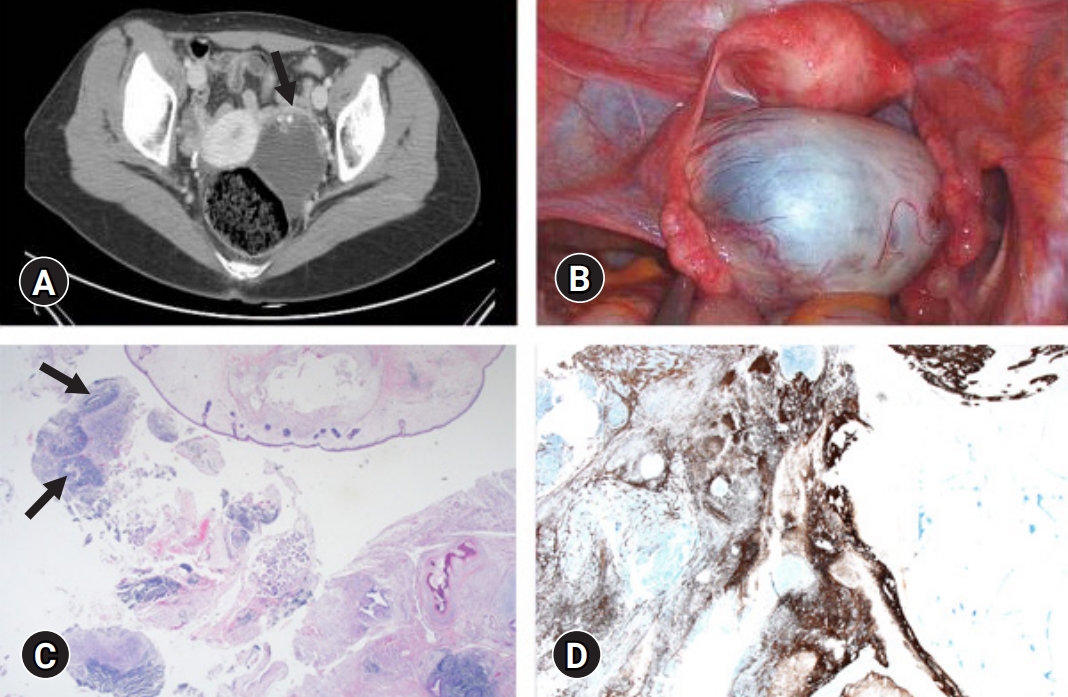
- Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis associated with ovarian teratoma in Korea: three case reports
- Jisun Lee, Seongwoo Kang, Hye Jin Chang, Yong Hee Lee, Joo-Hyuk Son, Tae Wook Kong, Suk-Joon Chang, Kyung Joo Hwang, Miran Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):350-355. Published online January 27, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00794
- 5,695 View
- 94 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) encephalitis is a severe autoimmune paraneoplastic syndrome associated with ovarian teratomas. Most patients develop neurologic symptoms, including psychosis, memory deficits, seizures, or abnormal movements, and experience abdominal pain related to ovarian neoplasm. We present a case report of three patients diagnosed with anti-NMDAR encephalitis accompanied by ovarian teratomas at Ajou University Hospital in Korea. The patients demonstrated a different clinical course of the disease. However, upon diagnosis, all patients underwent surgical removal of the ovarian teratoma followed by intensive immunotherapy. The symptoms progressively improved following treatment. This is a case report of a rare autoimmune anti-NMDAR encephalitis associated with ovarian neoplasms, including immature teratoma.
- Cardiopulmonary bypass preparation is mandatory in cardiac exploration for blunt cardiac injury patients: two case reports
- Shin-Ah Son, Joon Yong Cho, Gun-Jik Kim, Young Ok Lee, Hanna Jung, Tak-Hyuk Oh
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):356-360. Published online March 3, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00822

- 5,313 View
- 76 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Treating cardiac injuries following blunt trauma to the chest requires thorough examination, accurate diagnosis, and therapeutic plan. We present two cases; pulmonary vein rupture and left atrial appendage laceration, both as a result of blunt chest trauma. Through these cases, our team learned the importance of maintaining hemodynamic stability during the examination of injured cardiac structures. And based on the comprehensive cardiac examination, a decision to surgically intervene with median sternotomy via cardiopulmonary bypass was made, saving lives of the patient. This report introduces how such decision was made based on what supporting evidence and the diagnostic process leading to the initiation of surgical intervention. This report may help with decision-making process when confronted by blunt cardiac injury patients who need cardiac exploration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The role and timing of cardiopulmonary bypass in the surgical repair of traumatic cardiac injury
Mayo Kondo, Shinichi Ijuin, Tomonori Haraguchi, So Izumi, Reiko Kanno, Kazunori Sakaguchi, Kazumasa Edono, Haruki Nakayama, Satoshi Ishihara, Takuro Tsukube
General Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.2023; 71(10): 561. CrossRef
- The role and timing of cardiopulmonary bypass in the surgical repair of traumatic cardiac injury
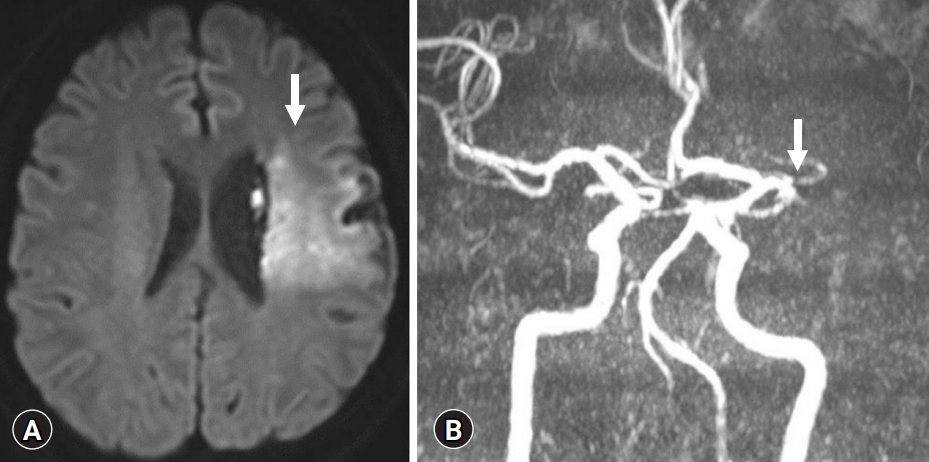
- Safety and effectiveness of early cardiac rehabilitation in a stroke patient with heart failure and atrial fibrillation: a case report
- Sang Cheol Lee, Eun Jae Ko, Ju Yeon Lee, Ae Lee Hong
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):361-365. Published online March 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00885
- 7,119 View
- 161 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Stroke patients have reduced aerobic capacity. Therefore, intensive structured exercise programs are needed. We report the case of a patient with stroke and cardiac disease who underwent early inpatient cardiac rehabilitation (CR). A 38-year-old male patient with atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and cerebral infarction underwent a symptom-limited exercise tolerance test (ETT) without any problems on day 45 after admission. He completed a 2-week inpatient program and an 8-week home-based CR program. Follow-up ETT showed increased exercise capacity. The present case might be the first to report a safely performed CR program in a patient with stroke and cardiac comorbidity in Korea. Systematic guidance is needed for post-stroke patients to receive safe and effective CR for the secondary prevention of stroke and cardiovascular risk.
- Pembrolizumab-related autoimmune hemolytic anemia in a patient with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma: a case report
- Dong Won Baek, Yee Soo Chae
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):366-370. Published online March 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2021.00899

- 5,164 View
- 120 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have become the main drugs for programmed cell death receptor-1 or ligand-1 expressing non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) combined with conventional chemotherapy. ICIs are generally more tolerable than cytotoxic chemotherapies in terms of toxicity, and ICI-related adverse events are mild and manageable. However, these drugs may lead to unexpected severe adverse events such as immune-related hematologic toxicities, which could be life-threatening. Here, a rare case of a pembrolizumab-related adverse event in a patient with NSCLC who showed early-onset hemolytic anemia and recovered by high-dose steroid and a series of plasma exchanges is reported.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Case Report: Life-threatening pancytopenia with tislelizumab followed by cerebral infarction in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma
Hang-Yu Gu, Jing-Wen Zhao, Yin-Shuang Wang, Zhuo-Nan Meng, Xiu-Ming Zhu, Fu-Wei Wang, Ai-Hong Zheng, Guo-Qing Wu
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunotherapy-associated Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
Steven R. Hwang, Antoine N. Saliba, Alexandra P. Wolanskyj-Spinner
Hematology/Oncology Clinics of North America.2022; 36(2): 365. CrossRef - Therapeutic plasma exchange in the management of immune checkpoint inhibitor‐associated immune‐related adverse effects: A review
Oluwatoyosi A. Onwuemene, Chizoba I. Nnoruka, Christopher J. Patriquin, Laura S. Connelly‐Smith
Transfusion.2022; 62(11): 2370. CrossRef - Diagnosis and management of cold agglutinin disease associated with low-grade B-cell lymphoma in a patient receiving pembrolizumab for lung cancer
Nabin Raj Karki, Peyton McElhone, Natasha Savage, Nagla Abdel Karim
BMJ Case Reports.2021; 14(8): e243751. CrossRef - Red Blood Cell Autoantibodies in Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Eungjun Yoon, Tae Yeul Kim, Sun Kyoung Mun, Duck Cho
The Korean Journal of Blood Transfusion.2021; 32(3): 201. CrossRef
- Case Report: Life-threatening pancytopenia with tislelizumab followed by cerebral infarction in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma
- Serotonin syndrome in a patient with chronic pain taking analgesic drugs mistaken for psychogenic nonepileptic seizure: a case report
- Mathieu Boudier-Revéret, Min Cheol Chang
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(4):371-373. Published online April 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2021.00948
- 5,080 View
- 201 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Serotonin syndrome (SS) is a potentially life-threatening condition that is caused by the administration of drugs that increase serotonergic activity in the central nervous system. We report a case of serotonin syndrome in a patient with chronic pain who was taking analgesic drugs. A 36-year-old female with chronic pain in the lower back and right buttock area had been taking tramadol hydrochloride 187.5 mg, acetaminophen 325 mg, pregabalin 150 mg, duloxetine 60 mg, and triazolam 0.25 mg daily for several months. After amitriptyline 10 mg was added to achieve better pain control, the patient developed SS, which was mistaken for psychogenic nonepileptic seizure. However, her symptoms completely disappeared after discontinuation of the drugs that were thought to trigger SS and subsequent hydration with normal saline. Various drugs that can increase serotonergic activity are being widely prescribed for patients with chronic pain. Clinicians should be aware of the potential for the occurrence of SS when prescribing pain medications to patients with chronic pain.

 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine


 First
First Prev
Prev



